(a) Absorbance (optical density) spectra of Au nanorods (AR = 3.7) in... Download Scientific
Optical Density Definition It is often said to be identical to the absorbance. It is a logarithmic ratio of the falling radiation to the transmitted radiation through a material. For a given wavelength, the expression of optical element transmittance is expressed as: Log 10 (1/T) Where T is transmittance. Few things to note:

Bisphenol A UVVIS absorbance spectrum in water (OD optical density). Download Scientific Diagram
For absorbance measurements, the optical density (O.D.) is a logarithmic measurement of the percent transmission (%T) and it can be represented by the equation, A = log10 100 / %T. Dr EJ Dell (8) Here is a graphical scale that represents this: Fig. 1: Graphic representation of the relation between absorbance and transmittance

Optical density values in terms of the absorbance of the aqueous... Download Scientific Diagram
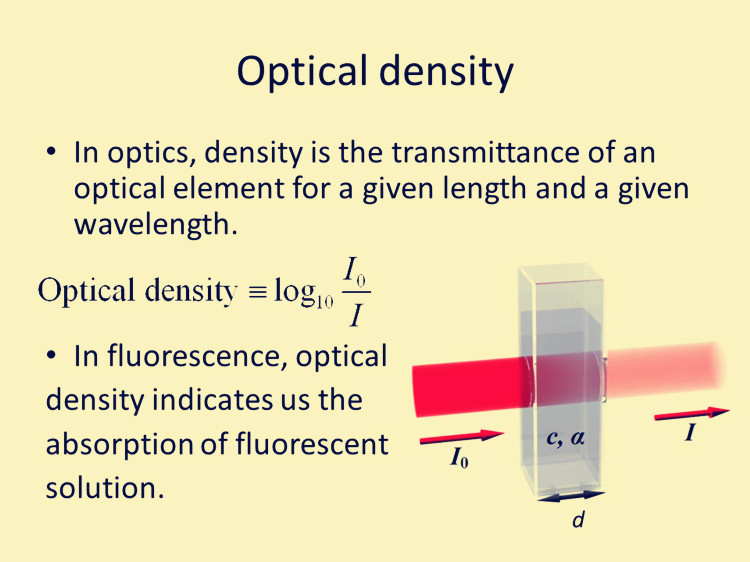
The optical density or absorbance of a material is a logarithmic intensity ratio of the light falling upon the material, to the light transmitted through the material: (5.76) where I0 and I1 are the intensities of the incident and transmitted lights, respectively.
Difference Between Optical Density and Absorbance Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
absorbance optical systems Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the optical system of the Beckman Optima XL-A Analytical Ultracentrifuge. and density of the solvent, relative to that of water at 20°C Svedberg unit (10-13 seconds) Standard entropy Temperature in Kelvin Time Velocity

Absorbance (optical density) of the different solgel photoelectrodes.... Download Scientific
Specsavers have made it easy to claim & help you get the most out of your optical extras. At Specsavers, you'll find a range of health fund offers you won't get anywhere else.

Measured optical density (OD should be considered as absorbance) for... Download Scientific
Optical density is referred to as the property of the material (transparent material) that basically deals with the measurements of transmission of light through the material. It is a unitless quantity. The density here is not the ratio of mass and volume. It is the measure of the compactness of particles in matter.

Opticaldensity (absorbance) spectra of (1) pure Ag nanoparticles and... Download Scientific
Optical density is a measure of how effectively a medium, such as a material or a solution, absorbs or transmits light. It is a property that describes the degree to which light is attenuated as it passes through the medium. The term "optical density" is also known as "absorbance," which is used interchangeably in many scientific.
Optical absorbance spectrum of the SWCNT layer. (a) The average... Download Scientific Diagram
Optical density times 10 is equal to a transmission loss rate expressed in decibels per cm, e.g., an optical density of 0.3 corresponds to a transmission loss of 3 dB per cm. Optical density is often defined without regard to the length of the sample; in this case it is a synonym for absorbance. Neutral density filters are typically quantified.
What Is Optical Density?
A material's optical density is the logarithmic ratio of falling radiation to transmitted radiation through it. It can also be defined as a fraction of absorbed radiation at a specific wavelength. The optical density of the medium determines the speed of light, which is determined by the qualities of the medium on which it is incident.

Standard optical density curves versus glucose concentration, measured... Download Scientific
An alternative term, which however is ambiguous, is optical density. Absorbance values often depend on the optical wavelength. Note that optical attenuation e.g. of a neutral density filter may not be entirely resulting from absorption, but at least partially from reflection; the term absorbance is then questionable.

Absorbance (optical density) of the different solgel photoelectrodes.... Download Scientific
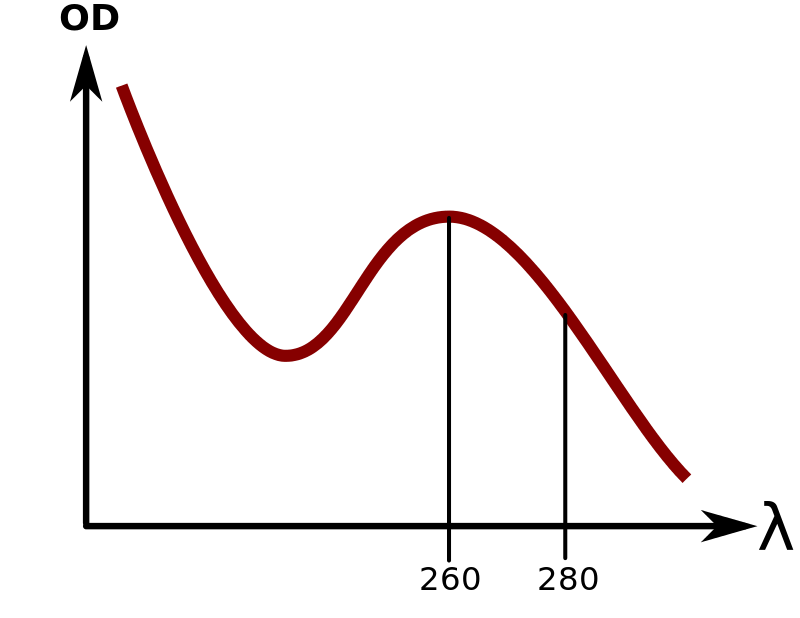
When a spectrophotometer gives you the absorbance A' on the logarithmic form, i.e. the optical density OD, which is a common output from many spectrophotometers (OD = A' = log10(1/T) = alog10.

Standard curve for SM absorbance. OD optical density. Download Scientific Diagram
Optical density measures how much a substance hinders the passage of light, while absorbance quantifies the light absorbed by a substance. Key Differences Optical density refers to the degree to which a material impedes the transmission of light, considering factors like reflection and scattering.

Biomass vs. Absorbance. Relation between Optical Density (Absorbance at... Download Scientific
Optical density is a measure of the absorbance or attenuation of light as it passes through a material or medium. When a beam of light is absorbed by atoms, the phenomenon of absorption occurs. The degree of absorption depends on the thickness of the sample and the concentration of absorbing atoms.

(a) Absorbance (optical density) spectra of Au nanospheres in paraffin... Download Scientific
The optical density is a property of a transparent material that measures the speed of the light through the material. The extent to which any optically dense medium bends transmitted light rays towards or away from the normal is called the optical density.

Transient absorption spectroscopy (TAS) optical density ΔOD vs.... Download Scientific Diagram
Optical density may mean the absolute value of the logarithm with base 10 of the power transmission factor of an optical attenuator (e.g. as used for a laser safety glass): Δ ν l a s e r = π h ν ( Δ ν c) 2 P o u t For example, an optical density of 3 means that the optical power is attenuated by the factor 10 3 = 1000.

e Calibration curves of optical density (595 nm) versus bacterial... Download Scientific Diagram
The reading, called absorbance or optical density, indirectly reflects the number of bacteria. This method is faster than the standard plate count but is limited because sensitivity is restricted to bacterial suspensions of 10 7 cells/mL or greater.. Describe how an absorbance can indicate the density of cells within a culture.